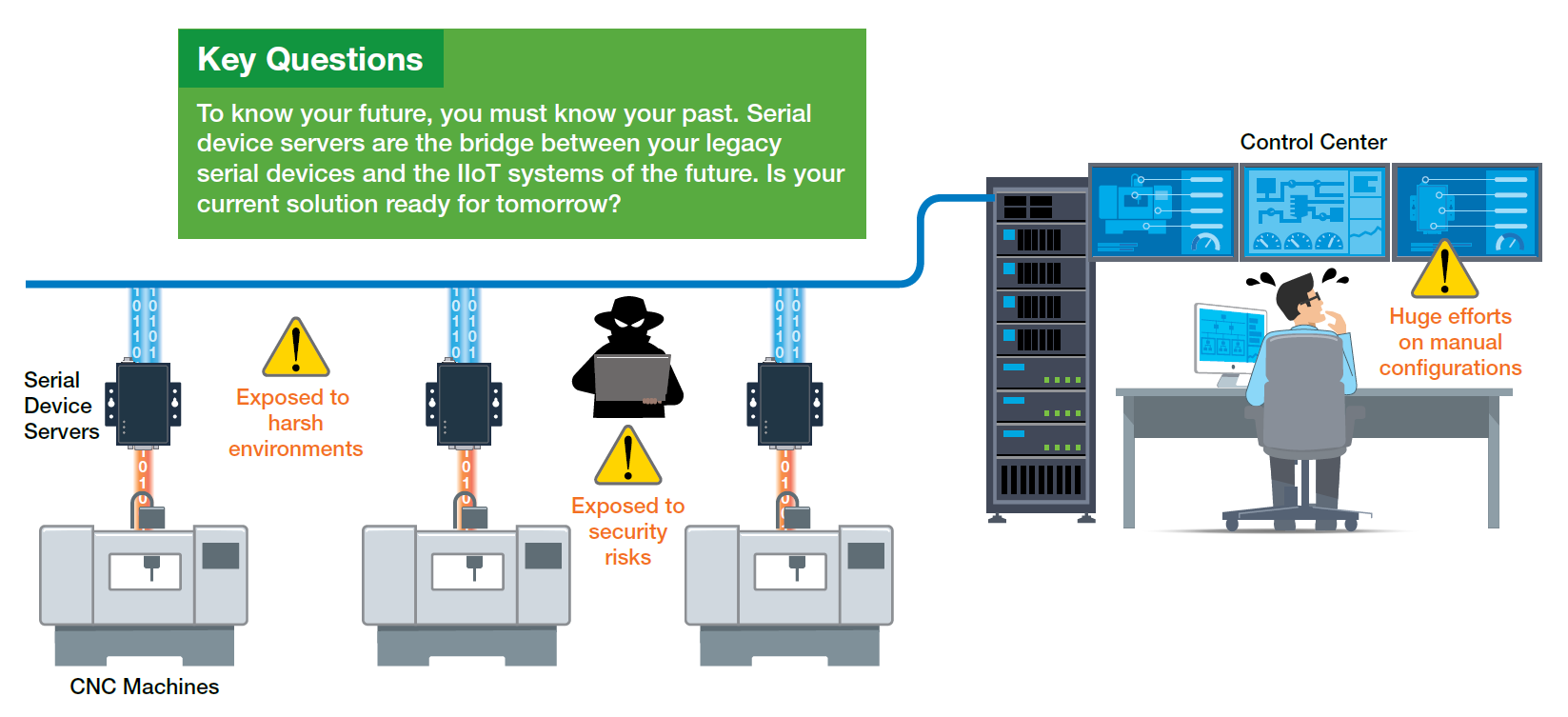
Instead of bidding farewell to all your faithful legacy devices to revamp your existing industrial automation system into a modern IIoT application, consider that your aging legacy devices are still serving a valuable purpose, and replacing them entirely can be costly.
While IIoT applications typically leverage SCADA systems using IP over Ethernet networks, your legacy devices likely rely on serial-based communications with fieldbus protocols, making them incompatible with IP communications. So, how can you facilitate the connection between legacy serial devices and Ethernet-based SCADA systems?
Although upgrading to newer Ethernet-based devices would resolve the communication issue, the cost and disruption of replacing all equipment can be prohibitive. For instance, replacing a serial-based CNC machine is not only expensive but also impactful on most businesses’ budgets. Furthermore, serial devices offer unique advantages. For example, RS-485 power meters enable multidrop communication, simplifying and enhancing wiring efficiency. Employing serial-to-Ethernet solutions between your serial devices and IP-based systems can help you save costs and effort while enjoying the benefits of both serial and Ethernet communication. In this guide, we will demonstrate how to select a suitable serial-to-Ethernet solution for your needs.
Key Considerations when Selecting Serial Device Servers
To integrate proprietary serial devices over IP networks, serial device servers serve as a straightforward bridge between your legacy serial devices and modern communication systems. However, without adequate understanding of serial device servers’ functionalities, selecting one can consume unnecessary time and effort. Here are three essential factors to bear in mind when picking a serial device server. If your legacy serial devices utilize standard fieldbus protocols like Modbus and PROFIBUS, check out our article for guidance on choosing the appropriate protocol gateway for enabling IP communications.
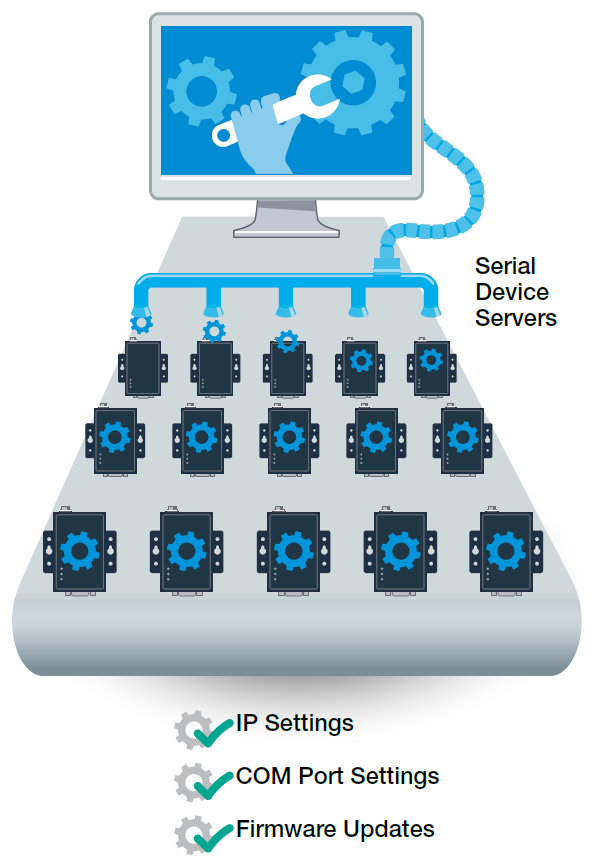
Maximize Each Progression
Comprehending and deploying serial device servers can be far more manageable than replacing all your dedicated legacy devices. However, configuring multiple serial device servers can be time-consuming, involving manual setup of numerous settings. Whether configuring IP addresses for each server, establishing virtual serial (COM) ports, or adjusting serial and Ethernet parameters, the configuration process can be arduous without clear instructions or an intuitive utility to guide you through the settings. The frustration can extend into operation, where managing or maintaining numerous devices becomes overwhelming.
While selecting a serial device server, ensure it offers a user-friendly web console or utility to streamline configuration and management. Overlooking this feature can complicate device management as your network expands. Replicating configuration tasks elevates the management burden and can be draining.
Safeguarding Your Networks in an Interconnected Environment
Previously, industrial automation primarily necessitated linking a restricted number of field devices within small, isolated, private networks. In the IIoT era, industrial applications demand connecting more field devices over public networks, enabling both OT and IT personnel to access field data. While enhancing field device accessibility yields numerous benefits, it also exposes networks to new security threats. Inadequate protection renders applications vulnerable. For instance, traffic controllers might become targets for hackers seeking to manipulate signals and create chaos on the roads. View our video to learn how to block unauthorized access.
Various entry points, including your serial device servers, can be used by individuals to access your application. Ensure the selected serial device servers incorporate robust security features to safeguard your data. Applying strong login credentials or setting up a whitelist are basic methods to restrict access to authorized personnel. Closing unutilized ports on serial device servers is another effective way to block exploitable entry points. During data transmission, employing a secure protocol like HTTPS can reduce unauthorized access to field data.
Remember the First “I” in “IIoT”
Are you still relying on commercial-grade serial device servers for your industrial applications? While satisfactory for limited or established field devices, these servers may not be suitable for IIoT projects managing a vast number of devices and transmitting critical field data promptly. Prioritize selecting a serial device server capable of enduring harsh conditions like extreme temperatures or high electromagnetic interference to minimize data loss from server shutdowns.

Assessing your serial device server options using these aforementioned criteria can lead you to the appropriate solution for your industrial applications. For instance, Moxa’s NPort serial device servers are designed with user-friendly, secure, and reliable features ideal for connecting field devices in IIoT applications. To delve deeper into industrial connectivity, download our E-book.
- Not Only for Automobiles: Discovering CANbus Technology in Various Industrial Settings - October 29, 2024
- Boost Your Network Performance: An Exciting Manual to PoE Switches! - September 10, 2024
- Understanding Gigabit Switches: Industrial vs Regular Gigabit - September 4, 2024




