Experts in the industry have cautioned that the current cloud-computing models utilized in numerous IIoT systems are not adequately equipped to handle the vast amount of data produced by the billions of IoT devices expected to come online in the near future. Additionally, these devices generate data in various formats using different protocols, which complicates their acquisition and real-time processing. In the following piece, we explore two alternatives to the cloud computing model—fog computing and edge computing, and delve into the reasons why organizations are investing in solutions based on these models.
Cloud Computing vs. Fog Computing vs. Edge Computing
Cloud computing within the context of IoT revolves around centralized data processing. In contrast, fog computing and edge computing models concentrate on relocating computational power, storage capacity, device-control capability, and networking power closer to the devices. The crux of a successful IIoT endeavor lies in opting for a computational model that aligns best with your organization’s requirements.
Fog computing, a concept coined by Cisco, refers to computing on devices situated in an intermediate layer known as the fog layer positioned between the cloud and the IoT edge devices. The fog layer encompasses fog nodes, essentially industrial controllers, gateway computers, switches, and I/O devices that offer computing, storage, and connectivity services. The fog computing model extends the cloud nearer to the edge of your network where the devices are located, fostering edge intelligence.
Edge computing mirrors fog computing, and both terms are often used interchangeably. Edge computing solutions embed intelligence into edge devices to enable local processing and analysis of data.
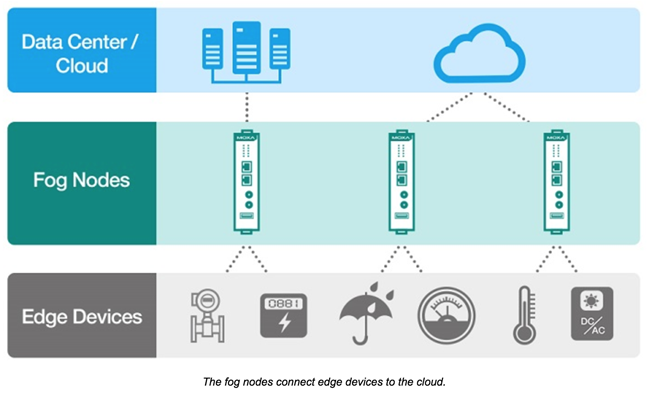
Here are some crucial factors to take into account when selecting a computational model for your IIoT.
Latency
Routing all device data to the cloud for processing and analytics can range from a brief few minutes to multiple days. For instance, if your IIoT devices are generating one terabyte (TB) of data per day, transferring this data to the cloud, processing it, and deriving actionable insights could take several days. By this point, the opportunity window to act on the data-driven conclusions may have already elapsed. Today’s business applications necessitate response times in the order of seconds or milliseconds. Time-critical applications, such as Industrial IoT, demand instant processing of device data to facilitate timely corrective actions. The fog computing model mitigates latency while enabling swift decision-making in comparison to the cloud computing model.
Data-transfer and bandwidth cost
Security
Autonomous operation in remote areas
Moxa Can Assist You in Embracing the New IIoT Trend
Moxa’s IIoT Gateway solution offers a shortcut for accelerating your IIoT initiatives. The solution comprises a UC-8112-LX Edge Computer, ThingsPro Gateway software, and ThingsPro Server software tailored to propel your IIoT projects for cloud-based applications and instill local intelligence at the edge. Moxa’s IIoT solution furnishes:
- Effortless integration of IT and OT systems
- Support for Modbus and MQTT protocols
- 4G communication support
- Built-in client interfaces for cloud services like AWS
- Secure connections through VPN
- C and Python APIs for localized data processing
- UC-8112 computer for local intelligence and control
- Future-proof design for seamless system expansion
Begin your IIoT development journey with Moxa’s IIoT Gateway Starter Kit. For more information, access the white paper.
- Not Only for Automobiles: Discovering CANbus Technology in Various Industrial Settings - October 29, 2024
- Boost Your Network Performance: An Exciting Manual to PoE Switches! - September 10, 2024
- Understanding Gigabit Switches: Industrial vs Regular Gigabit - September 4, 2024


