The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) and trends in the smart factory are reshaping the current OEM business strategy. Measures like Overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) and zero equipment downtime are no longer just popular terms; they are now essential benchmarks for business success. To deliver these services, equipment producers require an efficient method to gain insight into their machinery and have the ability to remotely link to and manage their machines at various sites. In this piece, we will delve into five crucial components of a secure remote access solution for industrial machinery and elaborate on why a cloud-based remote access system is optimal for equipment manufacturers.
Analogous remote access methods, such as a virtual private network (VPN) and remote desktop connection (RDC), have been delivering secure remote access to networks and systems in businesses. Nonetheless, several of these solutions lack the adaptability or intelligence to meet the specific requirements of industrial equipment makers. The five crucial elements that such equipment manufacturers need to take into account when working with VPN and RDC solutions are:
1. Setup Process that Consumes Time and Requires Extensive IT Acumen
Building connectivity with remote machines and exchanging the requisite authentication keys and data necessitate configuring multiple parameters. Setting up VPN and RDC connections is a convoluted and time-consuming process that demands extensive IT expertise.
2. Adjustments in Corporate Security Policies Needed for Enabling Remote Machine Access
VPN applications mandate a VPN server to possess a static public IP address, with certain network ports configured to allow inbound and outbound traffic. Most IT departments are hesitant to implement these alterations in their organization’s network due to potential network vulnerabilities and compromised security.
3. Complexity and High Expenses Associated with Ensuring Security of Remote Links
VPN connections between equipment manufacturers and machine operators typically establish site-to-site connections, providing manufacturers with remote access to all local devices within a plant’s network. To mitigate this security hazard, IT departments must establish separate end-to-end connections using VPN technology, which is costly and intricate, significantly inflating maintenance expenses.
RDC connections pose similar challenges by exposing computing equipment on the plant network to the wider public network, resulting in security vulnerabilities. Resolving these security concerns necessitates additional resources in terms of personnel, setup costs, and maintenance fees.
4. Managing VPN Security Is Complex
Enhancing security involves using distinct pre-shared keys or X.509 certificates for every VPN tunnel. Managing keys or certificates for a small number of VPN connections is feasible. However, as the number of VPN tunnels expands, managing these keys and certificates becomes increasingly arduous.
5. Expansion and Adaptability Come with Increased Costs
VPNs often impose restrictions on the number of VPN tunnels they can accommodate. As businesses expand and more machines and devices connect, necessitating a growing number of engineers to support operations, the volume of VPN connections required rises. Once this surpasses the VPN server’s capacities, manufacturers must deploy a new VPN server and repeat the time-consuming configuration procedure.
Due to the limitations and drawbacks of VPN and RDC-based remote access solutions, equipment manufacturers and machinery makers are actively seeking user-friendly, secure, adaptive, and scalable solutions to effectively oversee their machines and equipment remotely.
Cloud-Based Protected Remote Connection
Cloud-based remote access is an innovative form of remote access solution facilitating flexible access to field machines. The network structure of a cloud-based remote access solution consists of three key elements: a remote gateway, a cloud server, and client software. Remote gateways connect to field equipment to enable remote access and control. Client software is installed on the engineer’s PC. The cloud server can be deployed on a cloud-based platform like Amazon Web Service or Microsoft Azure. Both the remote gateway and client software initiate secure outbound connection requests to the cloud server. Post successful authentication on both ends, the cloud server connects the two requests.
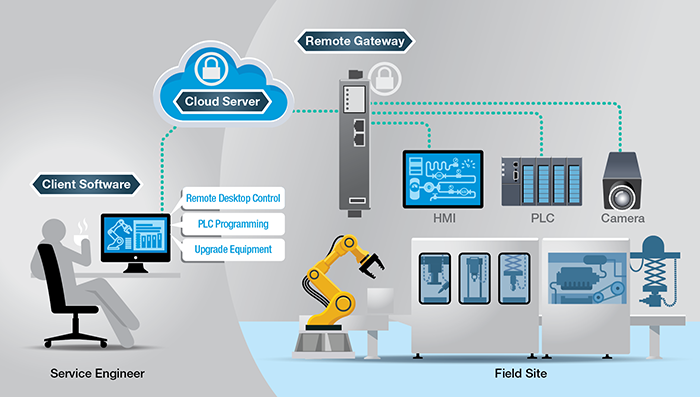
Moxa has crafted the Moxa Remote Connect (MRC) solution explicitly for OEMs and equipment manufacturers to optimize efficiency and reduce operational costs. For more information, visit Moxa Remote Connect and download our link to this white paper.
- Not Only for Automobiles: Discovering CANbus Technology in Various Industrial Settings - October 29, 2024
- Boost Your Network Performance: An Exciting Manual to PoE Switches! - September 10, 2024
- Understanding Gigabit Switches: Industrial vs Regular Gigabit - September 4, 2024


