Eliminating wired connections may not always be viable or optimal in every industrial setting. In scenarios where wiring or reconfiguring industrial operations proves challenging to meet market demands, industrial wireless LANs (WLANs) present a suitable alternative to traditional wired Ethernet LANs. The continuous evolution of wireless technology has significantly contributed to the widespread adoption of industrial WLANs in various sectors like automotive, logistics, and transportation systems. These industrial applications commonly involve automated machinery that is constantly on the move and hard to wire. The increasing acceptance of industrial WLANs facilitates the seamless interconnection of systems to enhance operational efficiency.
The burgeoning potential unleashed by cutting the cords has led to a rapid rise in the popularity of industrial WLAN applications in recent years. For example, deploying automated forklifts or overhead transfer systems in a smart warehouse using WLAN technology can boost efficiency and productivity, optimizing the utilization of available manpower. Despite the endless array of possibilities, the decision to go wireless isn’t always straightforward. Even after opting for a wireless LAN, how does one select the most suitable solution to meet specific industrial demands? Here are some key considerations to keep in mind.
Essential Factors to Consider When Selecting Industrial WLAN Devices
The expansion of connectivity beyond traditional boundaries with industrial wireless LANs opens up new avenues for exploration. Yet, industrial engineers may exhibit reluctance towards embracing wireless applications due to various challenges. How can one ensure that a network is truly connected when the connections themselves are invisible? And how does one troubleshoot when these unseen connections falter? These concerns are especially pertinent in the age of IIoT applications, where interconnected systems are crucial. A single point of failure could spell disaster for the entire network. In addition to meticulous planning of your wireless network design, here are some significant criteria for selecting industrial WLAN devices and addressing common concerns effectively.
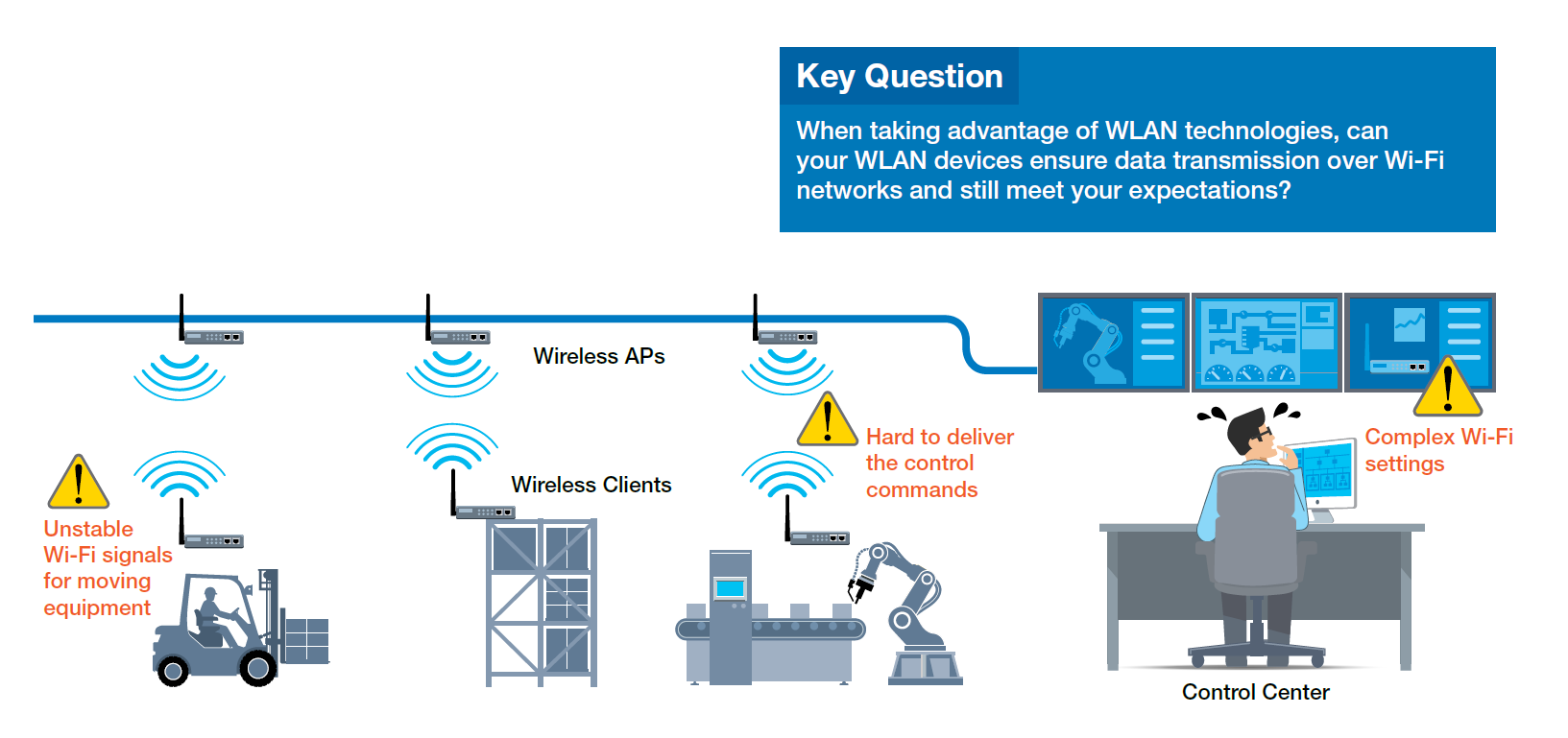
Priority on Wi-Fi Availability
Specialized technology is essential for industrial WLAN devices to establish and maintain reliable wireless networks. Factors like radio frequency (RF) interference in industrial environments, incorrect antenna setups, signal strength over long distances, and other issues can impact wireless connection quality significantly. Neglecting to address these concerns during system design can lead to communication instability, device damage, or complete system failures.
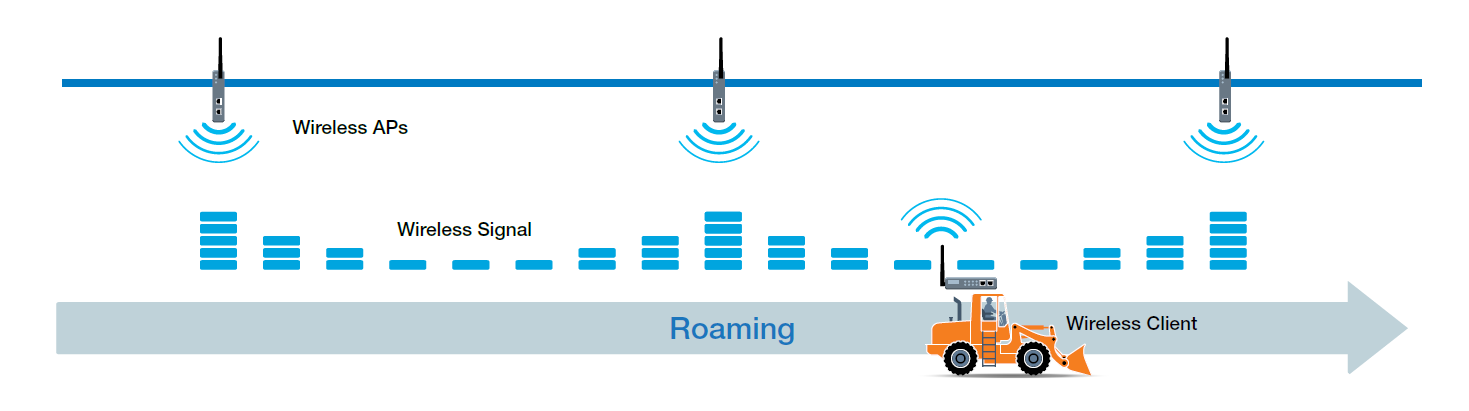
Furthermore, mobile equipment demands extra attention to roaming requirements. For example, a strong wireless signal at one location may require a stronger transmission signal if devices move to a different spot, causing slower Wi-Fi connections or even network interruptions. Given that sluggish or failed connections are unacceptable in industrial settings, advanced wireless roaming technologies should be considered to ensure seamless and reliable wireless connectivity.
Simplified Wi-Fi Configuration
Whether setting up a wireless network for the first time or managing multiple WLAN deployments, opting for user-friendly solutions is always advantageous. While wireless connections facilitate network infrastructure deployment, the ease of network setup and ongoing maintenance significantly influences the user experience. Employing a robust software tool for basic device configuration during initial setup or network maintenance can save substantial time and effort. Additionally, a tool that streamlines device configuration and identifies optimal Wi-Fi channels in the environment can keep wireless connections stable, simplifying network administration.
Overcome Protocol Compatibility Challenges
Various WLAN devices find deployment in diverse industrial settings, including automated guided vehicles (AGVs) and logistics forklifts. These systems rely on intricate devices like sensors and PLCs to track moving vehicles accurately. Seamless communication between PLCs and control centers is vital for safety. When wireless client devices, such as PLCs, connect in an industrial setup, ensuring support for specific industrial protocols like PROFINET becomes critical. To guarantee smooth industrial protocol communication, consider the following prerequisites:
- Layer 2 transparency over WLAN
- Communication latency meeting application requirements
These key criteria, honed over years of facilitating industrial connectivity globally, encapsulate essential considerations. For more insights on industrial IEEE 802.11n wireless AP/bridge/clients tailored to tackle industrial challenges, visit the Moxa website. To delve into industrial networking further, download our E-book.

- Not Only for Automobiles: Discovering CANbus Technology in Various Industrial Settings - October 29, 2024
- Boost Your Network Performance: An Exciting Manual to PoE Switches! - September 10, 2024
- Understanding Gigabit Switches: Industrial vs Regular Gigabit - September 4, 2024




