Industrial Control Systems Under Siege
The era of siloed “automation islands” for critical infrastructure and industrial networks is long gone. Nowadays, almost every crucial network or manufacturing setting faces cybersecurity threats due to the rising connectivity between IT and OT networks. A ransomware attack in August 2018 compelled Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC), the world’s largest semiconductor maker, to halt production lines, resulting in a loss of nearly US$86 million within 45 hours. Similarly, in March 2019, Hydro Norsk, one of the top aluminum producers globally, was targeted by a sophisticated ransomware attack, leading to a loss of around US$35 million in a week.
With enhanced connectivity comes increased vulnerability to cyber threats. The last decade witnessed a surge in cybersecurity incidents on operational technology (OT) and industrial control systems (ICSs).
| Year | Significant ICS Security Breaches | Targeted Sectors/Industries/Regions |
|---|---|---|
| 2010 | Stuxnet | PLC (Nuclear Power Plant in Iran) |
| 2011 | Duqu | Computer/Server (Public Utility in Multiple Countries) |
| 2012 | Disttrack/Shamoon | Computer/Server (Oil Company in Saudi Arabia) |
| 2014 | Sandworm | SCADA/HMI (Factory Floor in Multiple Countries) |
| 2015 | BlackEnergy/KillDisk | HMI/Serial Device (Power Grid in Ukraine) |
| 2016 | Industroyer | Circuit Breaker (Power Substation in Ukraine) |
| 2017 | Dragonfly | Computer/Server (Public Utility in US/EU) |
| 2018 | WannaCry | Computer/Server (Factory Machines in Asia) |
| 2019 | LockerGoga | Computer/Server (Aluminum Producer in Norway) |
| 2019 | DTrack | Computer/Server (Nuclear Power plant in India) |
Table: Overview of significant cyber incidents over the past decade1.
Targeted Sectors
Upon close inspection of the targets of these incidents, two primary industries stand out: critical manufacturing and critical infrastructure.
Critical manufacturing encompasses major companies like TSMC and Hydro Norsk, both essential links in the global supply chain. Cyberattacks on critical manufacturing entities have repercussions beyond financial losses to the organization; they can disrupt the entire global supply chain through a mere click or keystroke.
Critical infrastructure includes essential utilities for a nation’s energy, water, and transportation operations. A cyberattack that halts a nation’s infrastructure could have dire consequences on human lives and the environment. For instance, a 2016 cyberattack on a Ukrainian power substation left over 200,000 people without power for up to six hours in the midst of winter.
Addressing the Issue Holistically
As OT/ICS networks are no longer shielded from cyber threats, the pertinent question arises: how can we shield critical infrastructure and manufacturing systems from the mounting threat of cyberattacks? The solution is not straightforward. Rather, it necessitates a sustained commitment from all stakeholders in the public and private domains towards every facet of cybersecurity.
We examine six approaches through which the public and private sectors can fortify industrial networks.
Government Initiatives
Governments worldwide have emerged as key drivers behind the enhancement of cybersecurity in OT/ICS networks in recent times.
- In 2018, the United States government established the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency to streamline efforts in safeguarding the nation’s critical infrastructure and resources2.
- In 2018, the California state legislature passed SB-327, a law mandating IoT device manufacturers to integrate robust security features to protect user privacy and data stored on their devices3.
- In 2018, the European Commission enacted the Cybersecurity Act to reinforce the capabilities of the EU Agency for Network and Information Security (ENISA)4.
- In 2019, the Chinese government introduced MLPS 2.0, an updated version of the Multi-level Protection Scheme that extends cybersecurity regulatory oversight from conventional information systems to critical information systems, industrial control systems, and the Internet of Things.
Private Sector Initiatives
Despite entrenched business rivalries, OT users and solution providers in the private sector have banded together in various associations and coalitions to develop more effective security best practices.
- In 2019, the International Society of Automation (ISA) launched the Global Cybersecurity Alliance (GCA) to explore strategies for combating cyber threats in the era of IT/OT convergence5.
- Also in 2019, the Operational Technology Cyber Security Alliance (OTCSA) was established to offer comprehensive cybersecurity guidelines for operational technology. The members include OT operators like ABB and Wärtsilä, alongside IT/OT solution providers such as Check Point, Microsoft, and Qualys6.
Adherence to Open Standards and Guidelines
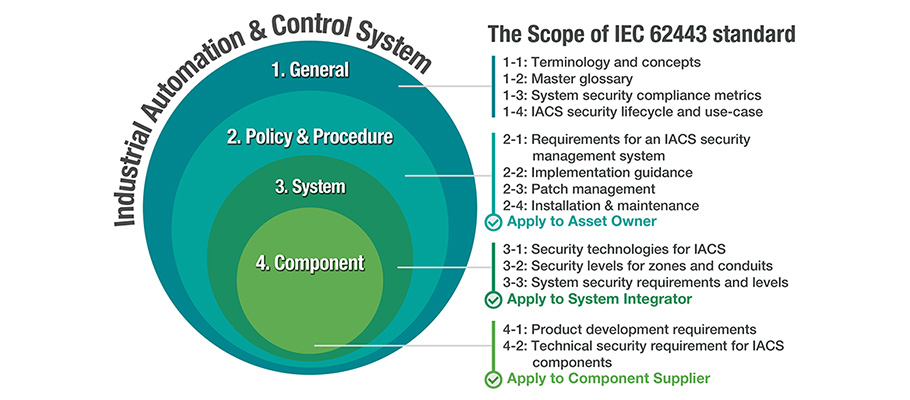
- IEC 62443
Recent private sector solution providers have been aligning around the IEC 62443 standards focusing on security capabilities for control system components. These standards furnish a versatile framework to counter present and future cybersecurity vulnerabilities in industrial automation control systems.
- IISF Report
The Industrial Internet Consortium (IIC) publishes the “Industrial Internet Security Framework (IISF) Report”, pooling the expertise of over 25 companies and academic institutions worldwide to offer comprehensive guidelines across diverse industries7.
The Future Belongs to Cybersecurity in OT/ICS
As evident from the escalating number of cybersecurity incidents involving critical infrastructure and manufacturing in recent times, a coordinated effort is imperative to ensure our present and future safety. Neglecting cybersecurity concerns for OT/ICS networks can impede the realization of the full potentials of digital transformation, regardless of advanced technologies like AI or big data. Governments and private sector solution providers worldwide have acknowledged the urgency of this issue and are collaborating to advance the cybersecurity agenda across the entire OT/ICS sector. Embedding cybersecurity into the core of OT/ICS requires more than just adopting new software or devices on your industrial network; it mandates integrating cybersecurity at every level of the organization.
For further insights on how governmental bodies and private sector entities can fortify industrial networks, kindly download the white paper.
1 Learn more by downloading the Moxa white paper: Industrial Network Cybersecurity: Debunking the Myths and Adopting Best Practices
2 https://www.us-cert.gov/about-us
3 https://leginfo.legislature.ca.gov/faces/billTextClient.xhtml?bill_id=201720180SB327
- Not Only for Automobiles: Discovering CANbus Technology in Various Industrial Settings - October 29, 2024
- Boost Your Network Performance: An Exciting Manual to PoE Switches! - September 10, 2024
- Understanding Gigabit Switches: Industrial vs Regular Gigabit - September 4, 2024