For automated material handling (AMH) systems like AS/RS and AGV to function effectively, they must have the adaptability to navigate their specified routes within a factory without hindrances while maintaining continual connectivity with the central control through a wireless setup. Furthermore, the control center needs a dependable wireless structure to oversee and manage the AS/RS and AGV setups along with sufficient bandwidth to relay data and directives to and from the systems, including live video feeds from IP cameras situated within these systems.
Choose the Appropriate Wireless Technology
When deciding on a wireless technology for your AS/RS or AGV setups, beyond the expenses, you should take into account the distance, speed, deployment intricacy, and frequency spectrum requisites for your application. Within a standard factory warehouse scenario, lanes might be spread across several hundred meters with mobile units swiftly traversing these paths for retrieval or storage tasks. WLAN technology proves to be the optimal choice for your AS/RS and AGV uses as it delivers ample coverage and can run within the 5 GHz frequency range. Nevertheless, meticulous planning and continuous optimization of your wireless infrastructure for mobile operations are critical to reap maximum advantages.
Recommendation 1: Strategize Prior to Rolling Out Your Wireless Solution
Since the wireless medium is intangible and functions over a frequency spectrum, it’s imperative to conduct a thorough analysis of the radio frequency spectrum to ensure that wireless transmissions occur within a reasonably clean environment with adequate signal reach. Failing to position access points (APs) in appropriate locations to guarantee sufficient coverage, employing the wrong antenna type, and neglecting interference mitigation are common issues observed in an impromptu network. It’s crucial to undertake a comprehensive site assessment and planning session to ascertain that the wireless system aligns with your application needs.
Recommendation 2: Verify Your Network Design
Once the planning phase is complete, the subsequent step is to employ wireless equipment to confirm the design. Begin with a small area and test your network blueprint. Utilize wireless sniffer tools within the range to track various Wi-Fi spots and plot the actual coverage profile of your network intend’s radio reach. Selecting the appropriate antenna and positioning it at the correct angle are essential for preventing blind spots along the mobile units’ path, thereby averting communication disruptions.
Recommendation 3: Install Antennas Correctly
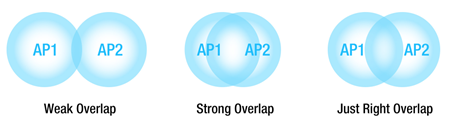
Picking the suitable antenna type for your APs and devices mounted on mobile units is a pivotal aspect in constructing a sturdy Wi-Fi grid. For APs, the options range from ceiling-mounted antennas, panel antennas, to di-pole omni-directional antennas, depending on the AP installation site. Concerning client devices affixed to AS/RS shuttles and AGVs, antennas can be placed on the vehicles’ tops or sides. Ensure there’s ample overlap between APs to foster as uniform communication performance as achievable.
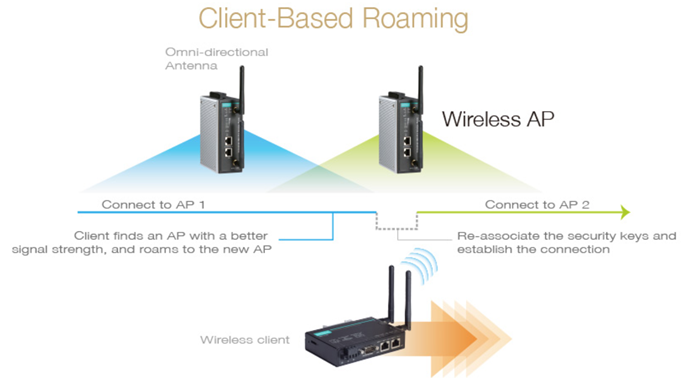
Recommendation 4: Optimize Your Network Parameters for Robustness in Mobile Environments
Post completion of wireless infrastructure deployment, further fine-tuning of the radios is imperative to enhance communication reliability and ascertain that the client radios on AGVs can seamlessly traverse among the APs without data loss, which could lead to operational downtime.
Recommendation 5: Deliberate on the Influence of Harsh Environmental Conditions
To optimize a wireless system’s performance, it’s essential to counteract the impact of the operational setting and assure that the electric components within your equipment can function devoid of interference. Some AGVs might operate in rigorous environmental conditions, such as within a frigid-storage warehouse where electrics must operate at sub-zero temperatures.
Another potential environmental challenge involves the stability of power motors on AGVs. The power supply on AGVs might not reliably provide consistent current to the radio apparatus with the optimum grounding path. Hence, applying isolation protection at the power input and potentially the antenna ports is crucial, as electrical disturbances could harm the mobile radios.
To dive deeper, retrieve the AS/RS and AGV white paper.
- Not Only for Automobiles: Discovering CANbus Technology in Various Industrial Settings - October 29, 2024
- Boost Your Network Performance: An Exciting Manual to PoE Switches! - September 10, 2024
- Understanding Gigabit Switches: Industrial vs Regular Gigabit - September 4, 2024


