Protocol transformation stands as a pivotal aspect of Industry 4.0. In manufacturing environments, engineers must guarantee seamless communication among a diverse array of devices utilizing a wide range of protocols. The typical approach to achieving this is through protocol transformation; the absence of which would significantly alter the landscape of factory automation.
As more manufacturing facilities transition to Industry 4.0, financial restrictions underscore the crucial role of protocol transformation. When implementing the necessary changes to institute a smart factory, replacing all existing legacy devices to facilitate connectivity from the network’s edge to the Internet can be cost-prohibitive. The optimal strategy involves prolonging the lifespan of these devices by enhancing their compatibility with contemporary equipment. Nevertheless, bridging the communication gap between a substantial number of legacy devices predominantly employing Modbus and the management systems like SCADA and PLCs, chiefly utilizing PROFINET and PROFIBUS, poses a notable challenge. This is where protocol gateways step in to aid system integrators (SIs) by delivering seamless protocol transformation, thereby enabling manufacturers to leverage the advantages of a smart factory.
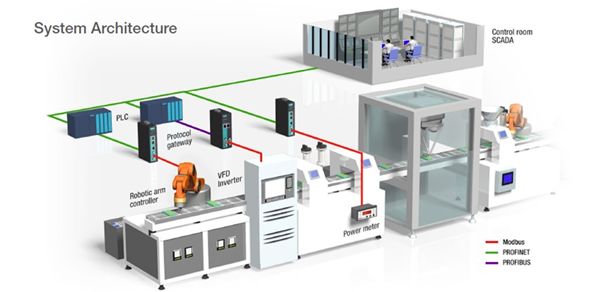
Contemporary factories necessitate the connection of numerous legacy devices, mainly employing Modbus, to interface with management systems like SCADA and PLCs, primarily running on PROFINET and PROFIBUS.
The market is teeming with protocol gateways, presenting engineers with a dilemma in distinguishing superior solutions amidst the array of offerings distinguished by communication methods, support for big data applications, configurations, and other functionalities. By and large, engineers should predicate their selection on the following criteria:
- Varied protocol transformations
- Rapid and straightforward configuration
- Incorporation of troubleshooting tools
- Versatility and scalability
Let’s delve deeper into these criteria.
Simple Deployment for Diverse Protocols
SIs regularly confront a multitude of processes necessitating distinct combinations of protocol transformations. Managing these processes with numerous gateway models dedicated to specific protocol transformations is time-consuming and adds complexity due to each gateway’s unique user interface design. Given the time-sensitive nature of engineering tasks, it is advisable to invest in a gateway that accommodates transformations for diverse protocol combinations. This approach can streamline deployment significantly, reducing installation and equipment expenses. The integrated advantage of an all-in-one design simplifies the task for less experienced engineers, who often possess limited protocol knowledge.
Efficient and Swift Configuration
Configuration can be a daunting endeavor, particularly when users are required to painstakingly configure detailed parameters one by one. Furthermore, engineers can attest to the frustration of spending hours configuring a gateway only to miss the mark on the first attempt. Gateways featuring user-friendly interfaces enable engineers to swiftly establish protocol transformation routines for most applications, saving considerable time when introducing new components to an existing system. Additionally, to mitigate the frustration of unsuccessful configuration attempts, a configuration wizard serves as a useful tool to guide engineers through accessing protocol transformation modes and completing configuration in a few effortless steps.
Simplified Troubleshooting
Instances of disrupted data transmissions often stem from erroneous command settings, disconnected cables, environmental noise, among other factors. Built-in troubleshooting functionalities, such as protocol diagnostics, traffic monitoring, status tracking, and fault prevention in protocol gateways, aid engineers in swiftly pinpointing and resolving such issues, curtailing downtime. An integrated protocol diagnostics and traffic monitoring tool furnishes engineers with expedited access to identifying the root cause of a problem by logging the data transmitted through the gateway and presenting detailed information like an alive list, counter, command results, etc. Additionally, a status monitoring feature provides insights on field device statuses and alerts the SCADA system if a slave device fails to respond, while a fault prevention mechanism dispatches predefined settings to field devices to avert erroneous downstream actions in case of upstream connection loss.
Versatility and Scalability
Integrating protocol gateways into distributed network architecture yields substantial advantages in terms of flexibility and scalability. Traditional PLC communication modules appended to PLCs to interface with distributed field devices encounter limitations due to their star topology, such as constraints on the number of racks. Leveraging stand-alone gateways that combine an extensive array of field devices eases wiring complexities, consequently reducing cable costs and enhancing scalability. Engineers also save considerable programming time when dealing with PLCs.
About Moxa
Moxa recently introduced the MGate 5103 and MGate 5111 gateways, facilitating prompt protocol conversions between Modbus devices and PROFINET/PROFIBUS-based SCADA or PLC systems. The MGate 5103 converts an array of protocols like Modbus RTU/ASCII/TCP to PROFINET, while the MGate 5111 performs the same conversions for PROFIBUS. Furthermore, the MGate 5103 and MGate 5111 assist in integrating EtherNet/IP PLCs into PROFINET or PROFIBUS systems. For further insights on the benefits of these gateways, please visit our site.
- Not Only for Automobiles: Discovering CANbus Technology in Various Industrial Settings - October 29, 2024
- Boost Your Network Performance: An Exciting Manual to PoE Switches! - September 10, 2024
- Understanding Gigabit Switches: Industrial vs Regular Gigabit - September 4, 2024


