Monitoring water distribution and wastewater treatment may not be considered glamorous, yet these services are vital for our daily lives. Whether you are turning on the faucet, taking a shower, or flushing the toilet, wastewater must be transported to a treatment plant to prevent contamination before it is released back into the environment. While we may not often think about how fresh water reaches our taps, municipal services play a critical role in ensuring the proper flow of sewage and wastewater away from our homes and streets.
Understanding the flow of water through pipes is just one aspect of the process. Water management services must constantly monitor thousands of miles of pipelines for leaks, corrosion, and blockages. Typically, engineers respond to reported issues, but quickly identifying and resolving leaks in remote locations can be challenging. Repairing water pipes often takes two to three days, during which time water or wastewater may leak into the environment.
A Smart IIoT-Based Monitoring Solution
To address these challenges, a municipal water management company developed an intelligent IIoT-based remote monitoring solution to detect and address water and wastewater leaks, pipeline corrosion, and sewage blockages more effectively. Remote I/O devices were strategically placed along the pipeline to gather data from a multitude of sensors measuring temperature, pressure, flow, and PH levels. This data was then transmitted to an IIoT edge gateway via Ethernet communications. The gateway, housed in an outdoor cabinet, sent the data over cellular networks to a remote monitoring system hosted on a private cloud server.
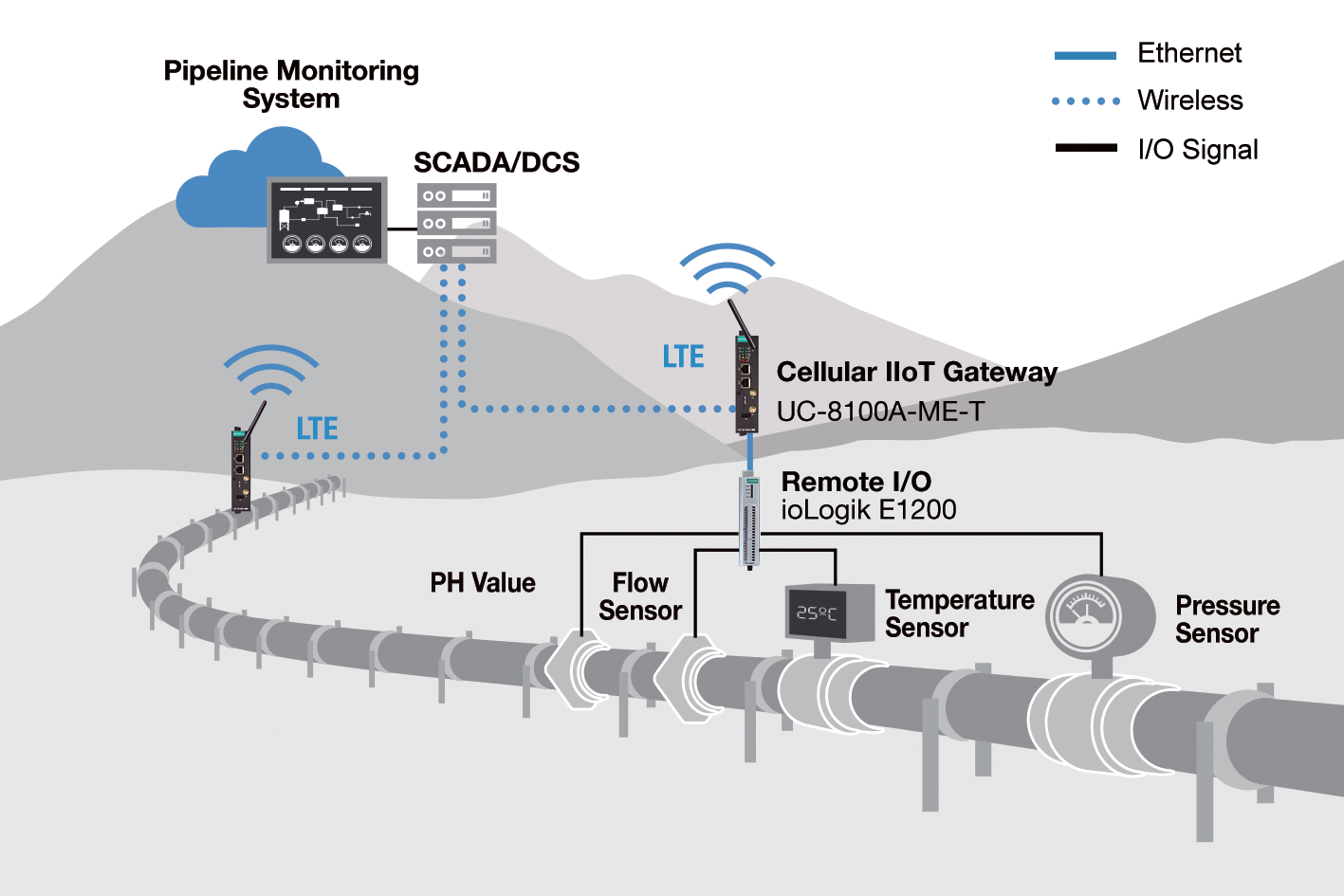
Designed for Challenging Environments and Compact Cabinets
Given that the IIoT edge gateways had to operate in small outdoor control cabinets exposed to harsh conditions and powered by solar panels, the compact size, wide temperature range, and low power consumption of Moxa’s UC-8100A-ME-T Arm Linux IIoT edge gateway were ideal for the project. In this setup, the ioLogik E1200 remote I/O device gathered sensor data and sent it to the UC-8100A-ME-T IIoT edge gateway in Modbus TCP format. With a 1 GHz Arm-based processor and 1 GB of RAM, the edge gateway efficiently processed data while consuming just 10 W of power. Additionally, the integrated cellular LTE connectivity in the gateway removed the need for a separate cellular gateway, reducing deployment costs and cabinet space. Moxa also offered prebuilt APIs and a cellular management utility, streamlining the integration process and reducing engineering efforts.
By utilizing these IIoT solutions to relay real-time data from multiple sites in a vast water pipeline network to a centralized SCADA system, the water management company could monitor pipeline statuses remotely through a dashboard hosted on its private cloud. These solutions significantly expedited the detection and repair of leaks, corrosion, and blockages, ensuring uninterrupted water flow.
If you want to explore more about Moxa wireless IIoT gateways and other case studies, you can access our Cellular and Wi-Fi IIoT Gateway Application Guidebook.
- Not Only for Automobiles: Discovering CANbus Technology in Various Industrial Settings - October 29, 2024
- Boost Your Network Performance: An Exciting Manual to PoE Switches! - September 10, 2024
- Understanding Gigabit Switches: Industrial vs Regular Gigabit - September 4, 2024


