To simplify the connectivity over extended distances and enhance centralized control in command centers, many enterprises are upgrading their current setups to IP-based networks. They are linking their devices and applications, like video surveillance, to the web. However, in the era of the IIoT, making network deployments and updates more straightforward has become a significant issue for technicians. Additionally, system improvements usually demand substantial investments in fresh cables. As an alternative to buying new cables, industrial Ethernet extensions enable users to elongate Ethernet networks beyond 100 meters using 2-wire copper cables to cater to various project needs, particularly for long-distance communication. In this write-up, we will touch upon four situations where Ethernet extensions enhance operational effectiveness.
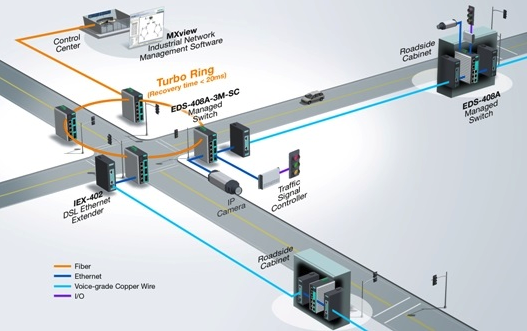
Case 1: Ensuring minimal disruptions for users
For instance, in the transport domain, traffic managers often need to update traffic management systems to transmit data to an operational control hub. Concurrently, they need to minimize potential disturbances such as construction or maintenance work on “road users,” encompassing pedestrians and vehicle passengers. System upgrades frequently involve incorporating video surveillance, necessitating increased bandwidth as a fundamental requirement. Industrial Ethernet extensions facilitate point-to-point communication over long distances through existing copper-wire frameworks and plug-and-play setups, expediting and simplifying network deployment. These extensions also support higher data transmission rates, rendering them suitable for data-heavy applications.
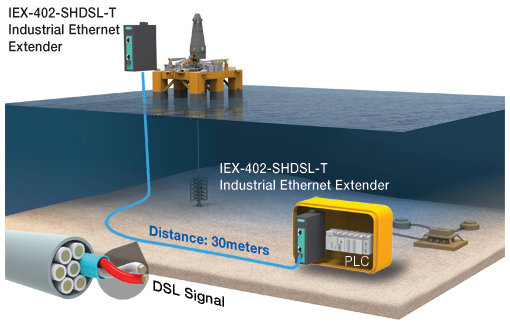
Case 2: Managing specific cabling in an application’s surroundings
In hazardous scenarios typical in sectors like oil & gas and mining, optical fiber cabling is unsuitable for networks as these cables are prone to damage or present risks due to cable splicing during extensions. Furthermore, environment-specific cables are usually deployed in challenging settings. For ventures requiring such cables, industrial Ethernet extensions empower users to efficiently establish or expand a network between a control hub and a challenging field location where expedited deployment and the capability for remote monitoring and device management are imperative. An industrial Ethernet extension supporting a bypass function and remote management substantially bolsters system reliability in mission-critical applications. To illustrate, an oil organization in Australia harnessed industrial Ethernet extensions to effectively establish a subsea oil and gas control system.
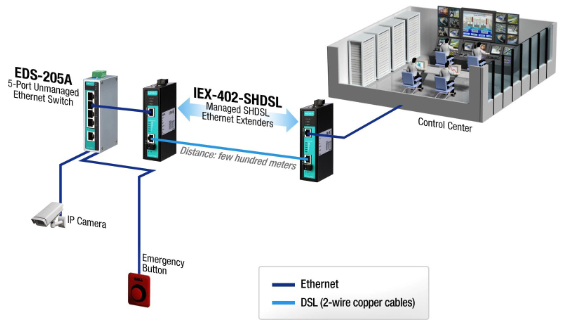
Case 3: Upgrading to a Wider Bandwidth Network
If an infrastructure of 2-wire copper cables is already in place, and you intend to modernize your legacy system to facilitate connecting more devices and subsystems, then industrial Ethernet extensions are the apt solution. They allow you to efficiently and swiftly upgrade the system on the existing infrastructure. For instance, a hospital in Hong Kong established an IP-based emergency alert setup in a ward, linking it to the facility’s advanced emergency network. Given the hospital’s use of 2-wire copper cables for communication in legacy systems, industrial Ethernet extensions seamlessly facilitated the establishment of the new emergency alert scheme.
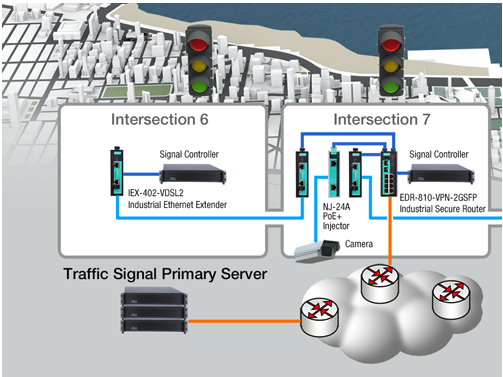
Case 4: Updating the legacy system to an IP-based network within tight financial constraints
The IIoT impelled businesses to transition their legacy systems to IP-based networks to enable universal connectivity and management via the internet. However, engineers are also constrained by budgetary limitations. To mitigate costs, the optimum solution is leveraging industrial Ethernet extensions. To exemplify, traffic supervisors recently shifted to IP-based traffic control systems at intersections with an integrated CCTV surveillance system over the same network. Installing Ethernet cables from one intersection to another wasn’t viable owing to cost restrictions and the lengthy distances between intersections. Consequently, network engineers opted to leverage the existing 2-wire copper cables and stretched their connectivity from one to two kilometers between intersections using industrial Ethernet extensions.
- Not Only for Automobiles: Discovering CANbus Technology in Various Industrial Settings - October 29, 2024
- Boost Your Network Performance: An Exciting Manual to PoE Switches! - September 10, 2024
- Understanding Gigabit Switches: Industrial vs Regular Gigabit - September 4, 2024


