Being one of the widely used methods of mass transit, trains play a vital role in cities undergoing rapid urbanization. With the ongoing digitalization of rail operations, train operators can utilize, create, and boost various applications like monitoring and control for rail systems. Ethernet train backbone networks are commonly employed for enabling communication between devices and systems on trains and linking diverse IP systems. Despite the numerous benefits associated with the use of Ethernet-based network systems, a drawback is that it makes networks more exposed to cyber threats.
As per the 2017 report on Securing Industrial Control Systems by SANS Institute, the primary concerns of end users are unauthorized addition of devices to networks, internal risks such as inadvertent human errors, and external threats posed by hackers. Cybersecurity is essential, but there is still a need for train operators to acquire more knowledge on how to mitigate these risks. Several relevant security standards providing comprehensive guidelines and recommendations are already in place for the industry. Among these, the ISA99/IEC 62443 stands out as the most widely cited industrial security standard, and the EN 50159 standard entails specifications on safety-oriented network communications catering specifically to rail systems. The ideal security approach involves enhancing each connected device in accordance with the directives outlined in these security standards. However, doing so may not always be feasible due to the associated high costs and maintenance efforts.
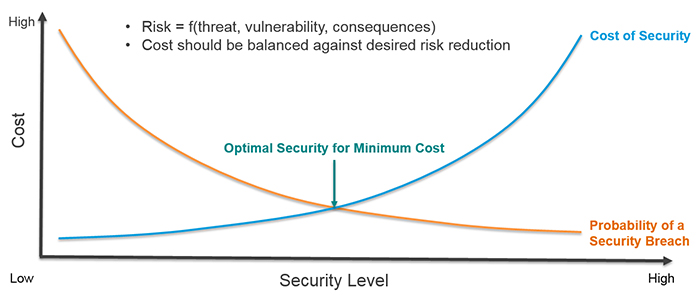
To streamline security measures onboard trains, it is crucial to explore if there are any general principles that train operators can rely on when fortifying network security. Keep reading to unearth the four most vital recommendations from cybersecurity specialists in the rail sector.
Securing rail networks demands robust network communications integrated with advanced security features, a protective layered design for wireless networks, a defense-in-depth secure network structure, and, not to forget, user-friendly network management software. It is paramount to ensure the effective implementation of these countermeasures to safeguard rail networks against cyber threats.
Advanced Security Features
The most efficient way to enhance device security is by ensuring that their settings cannot be tampered with in a manner that jeopardizes the devices and, ultimately, the network. Many cybersecurity experts regard the IEC 62443 standard as the most pertinent publication on securing devices in industrial networks. Here are the key priorities that should be enforced on network devices deployed within the rail industry.
• Authorization
One of the initial steps to take in enhancing security is to guarantee that only authorized individuals can modify network settings. Account management is often overlooked as it is relatively simpler to share identical login credentials among all network administrators. However, this could pose a significant vulnerability if malicious actors are given an opportunity to compromise the network.
• Network Access Control and Authentication
Access control can be enforced through authentication to ensure that the right person has the appropriate access level to modify network settings. Without access control or authentication mechanisms in place, it’s akin to leaving a gate wide open, granting unrestricted access to critical areas.
• Data Integrity and Confidentiality
When multiple devices and systems are interconnected on the network, and when data is crucial for monitoring or controlling rail systems, it is imperative that data is transmitted securely and safely. Various means can be employed to ensure data integrity, such as utilizing SSL or VPN.
• Layered-Design Protection for Wireless Networks
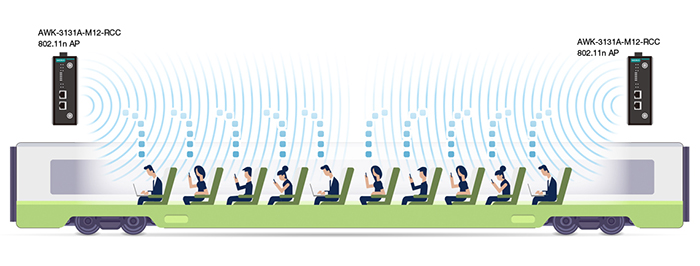
Train passengers expect to have access to reliable onboard Wi-Fi networks. Rail operators typically provide this as an optional service for passengers willing to pay extra for it. Nevertheless, this poses risks. When passengers’ devices connect to onboard APs, all of them share the same network, making it easier for malevolent individuals to pilfer personal data from other passengers. Hence, wireless client isolation is indispensable to prevent personal devices of passengers from directly communicating with each other on the same network.
Defense-in-Depth Secure Network Infrastructure
During network designing, many system operators have noted that employing defense-in-depth security architecture is one of the most effective strategies to secure a network. This architecture is devised to safeguard individual zones and cells. The initial step in constructing a defense-in-depth rail system involves segmenting networks to isolate traffic, thereby shielding against deliberate cyber attacks or human fallibility. By employing firewalls, network administrators can define zone-to-zone interactions to scrutinize network traffic. Based on the requirements of train operations, networks can be preconfigured to permit communications solely between specific devices or zones to mitigate security risks.
User-Friendly Network Management for Security Monitoring
Upon verifying that network devices and topology are secure, it is imperative to establish a network management protocol to enable system operators to obtain a comprehensive overview of the network’s security status. Addressing these security concerns before train deployment is crucial as substantial penalties could be imposed on train companies if trains are forced to halt mid-journey. Therefore, train operators must leverage network management software to gain insights into the security status of the network. Once operators have a clear picture of the network’s security status, it becomes easier to pinpoint areas that necessitate improvements to preempt cybersecurity threats from materializing.
Moxa furnishes network devices equipped with security features conforming to the IEC 62443 cybersecurity standard, along with security management functionalities like RADIUS authentication that aid in thwarting unauthorized access, known vulnerabilities, and unidentified attacks. Additionally, to safeguard the expanding onboard networks, Moxa offers all-in-one secure routers integrating firewall, VPN, and NAT capabilities to help train operators segment rail networks and shield critical data from potential risks. Moxa also supplies onboard wireless APs supporting client isolation to provide an additional layer of protection to wireless networks. For additional details, please reach out to us.
- Not Only for Automobiles: Discovering CANbus Technology in Various Industrial Settings - October 29, 2024
- Boost Your Network Performance: An Exciting Manual to PoE Switches! - September 10, 2024
- Understanding Gigabit Switches: Industrial vs Regular Gigabit - September 4, 2024


